

Cory Anger, Global Head of ILS Structuring, GC Securities*
Public entities' use of capital markets-based risk transfer capacity for the assumption of natural disaster losses, such as the cost of emergency relief and infrastructure and property damage has demonstrated success in de-risking public sector balance sheets. Capital markets innovators are beginning to leverage the outcomes achieved in the natural disaster sphere to other types of public sector severity losses, notably pandemic diseases. The capital markets may help fund resources to rapidly contain the spread of a pandemic, share the burden of associated medical expenses and/or manage the financial impact of the higher mortality rates.
According to the World Bank, (1) "there is a high probability that the world will experience a severe outbreak in the next ten to fifteen years that could destabilize societies and economies. Recent economic work suggests that the annual global cost of moderately severe to severe pandemics is roughly USD 570 billion, or 0.7 percent of global income. The cost of a severe pandemic like the 1918 Spanish flu could total as much as five percent of global gross domestic product."
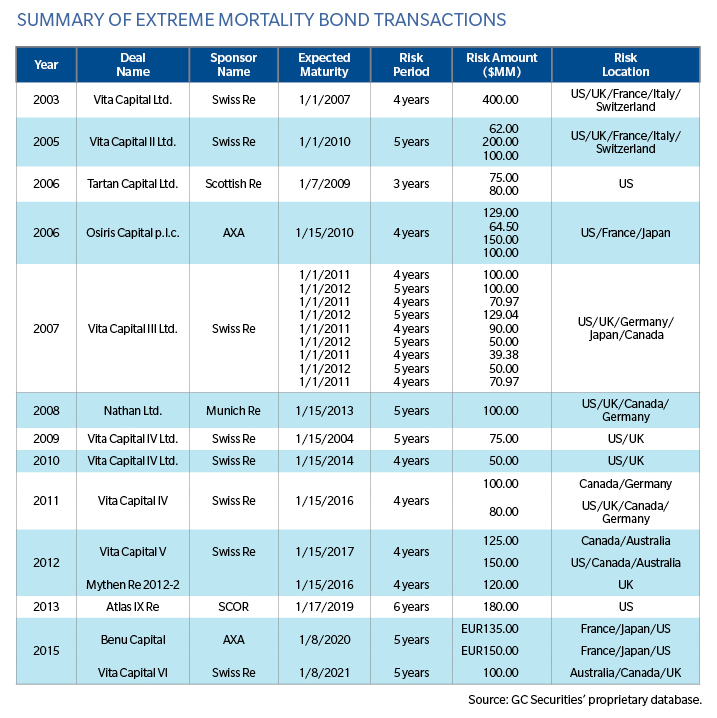
Alternative capital has already demonstrated its ability to provide extreme mortality protection to life (re)insurers; since 2003, more than USD 3.5 billion of extreme mortality catastrophe bonds were completed. While historical extreme mortality catastrophe bond structures have responded to all causes of extreme mortality, the bonds' trigger level for protection to respond generally focuses on the severe mortality impact from pandemics.
The table below provides a summary of extreme mortality catastrophe bonds completed to-date:
As investors become comfortable with pandemic risk, alternative capital is beginning to pivot its capacity to providing more action oriented pandemic protection during the beginning or ongoing phases of a pandemic (2) rather than focusing solely on replenishing capital post-event. Alternative capital also has the ability to provide multi-year protection when interim response structures are important for governmental organizations such as development banks, health organizations and sovereigns, to rapidly manage the needed monetary support. The goal is to contain and mitigate epidemics at their origin and prevent their potential global migration. The migration may impact key industries (tourism, hotels and transportation) and government budgets.
Recently, the World Bank Group (3) collaborated with the World Health Organization and other public and private sector partners to create the Pandemic Emergency Financing Facility (PEF) "to provide surge funding to prevent rare, high severity disease outbreaks from becoming more deadly and costly pandemics. The PEF is intended to be financed through insurance and cash based on the resources of the reinsurance market and the proceeds of catastrophe bonds (capital-at-risk notes) issued by the International Bank of Reconstruction and Development (IBRD)."
Alternative capital can provide protection for interim response structures that focus on managing morbidity and other healthcare costs (which can equally affect government healthcare programs, private healthcare plans and hospitals/medical facilities) for treatment for afflicted individuals, containing the spread of pandemic and for cleaning and disinfecting potential contaminated sites.
The growing use of alternative capital sources for assuming pandemic-related risks brings a more meaningful pool of capital to help health organizations, development banks, sovereigns, local governments and private industry better manage the impact of pandemics - globally, one of the most underinsured risks.
Note:
1. http://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/pandemics/brief/pandemic-emergency-facility-frequently-asked-questions
2. "Interim response structures."
3. http://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/pandemics/brief/pandemic-emergency-facility-frequently-asked-questions
*Securities or investments, as applicable, are offered in the United States through GC Securities, a division of MMC Securities LLC, a US registered broker-dealer and member FINRA/NFA/SIPC. Main Office: 1166 Avenue of the Americas, New York, NY 10036. Phone: (212) 345-5000. Securities or investments, as applicable, are offered in the European Union by GC Securities, a division of MMC Securities (Europe) Ltd. (MMCSEL), which is authorized and regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority, main office 25 The North Colonnade, Canary Wharf, London E14 5HS. Reinsurance products are placed through qualified affiliates of Guy Carpenter & Company, LLC. MMC Securities LLC, MMC Securities (Europe) Ltd. and Guy Carpenter & Company, LLC are affiliates owned by Marsh & McLennan Companies. This communication is not intended as an offer to sell or a solicitation of any offer to buy any security, financial instrument, reinsurance or insurance product.